The Role of Central Bank Independence in US Policy
3 min read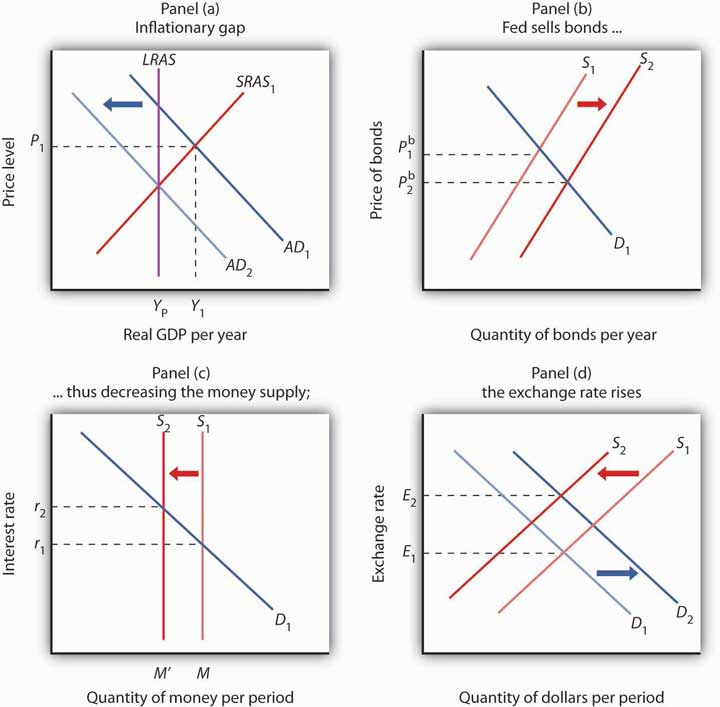

The Impact of Fed Policy on US Dollar Strength
Introduction
Monetary policy in the United States, managed by the Federal Reserve, plays a pivotal role in shaping the strength of the US dollar. The Fed’s decisions regarding interest rates, quantitative easing, and other policy tools have far-reaching consequences for the exchange rate of the dollar against other currencies. Understanding how these policies influence the dollar’s value is crucial for businesses, investors, and policymakers alike.
Interest Rate Dynamics
One of the primary tools the Federal Reserve uses to influence the strength of the US dollar is adjusting interest rates. When the Fed raises interest rates, it tends to attract foreign investment, as higher rates offer better returns on investments denominated in US dollars. This increased demand for the dollar can lead to its appreciation relative to other currencies. Conversely, lowering interest rates can weaken the dollar as it becomes less attractive to investors seeking higher yields.
Quantitative Easing and Dollar Liquidity
In addition to interest rate adjustments, the Federal Reserve has employed unconventional measures such as quantitative easing (QE) to stimulate the economy during times of crisis. QE involves the purchase of government securities and other financial assets to inject liquidity into the financial system. While QE can help boost economic activity, it can also put downward pressure on the US dollar by increasing its supply in the market.
Global Economic Factors
The strength of the US dollar is also influenced by global economic factors. In times of global uncertainty or economic instability, investors often seek safe-haven assets, including the US dollar. This increased demand can cause the dollar to appreciate, regardless of the Fed’s monetary policy actions. Additionally, trade imbalances and geopolitical events can impact the dollar’s value relative to other currencies.
Market Expectations and Forward Guidance
The Federal Reserve’s communication with markets and the public, known as forward guidance, can also affect the US dollar. When the Fed signals its intentions regarding future monetary policy actions, it can influence market expectations and investor behavior. For example, if the Fed indicates that it plans to raise interest rates in the future, investors may adjust their portfolios accordingly, affecting the dollar’s exchange rate in the present.
Inflation Targeting and Currency Stability
Maintaining price stability is one of the Federal Reserve’s primary objectives, and its inflation-targeting framework plays a crucial role in shaping expectations about future inflation. A credible commitment to low and stable inflation can help support the value of the US dollar by preserving its purchasing power over time. Conversely, concerns about inflation or deflation can lead to fluctuations in the dollar’s exchange rate.
Conclusion
The strength of the US dollar is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions, global economic conditions, market expectations, and inflation dynamics. Understanding these dynamics is essential for businesses, investors, and policymakers seeking to navigate the intricacies of the foreign exchange market and manage currency risk effectively. By staying informed about the factors that drive the value of the dollar, stakeholders can make more informed decisions to protect and enhance their financial interests in an increasingly interconnected global economy. Read more about monetary policy in usa